Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish hit
Polish products made of wood – furniture, window and door frames, yachts or paper and packages – these are real hits of the market.
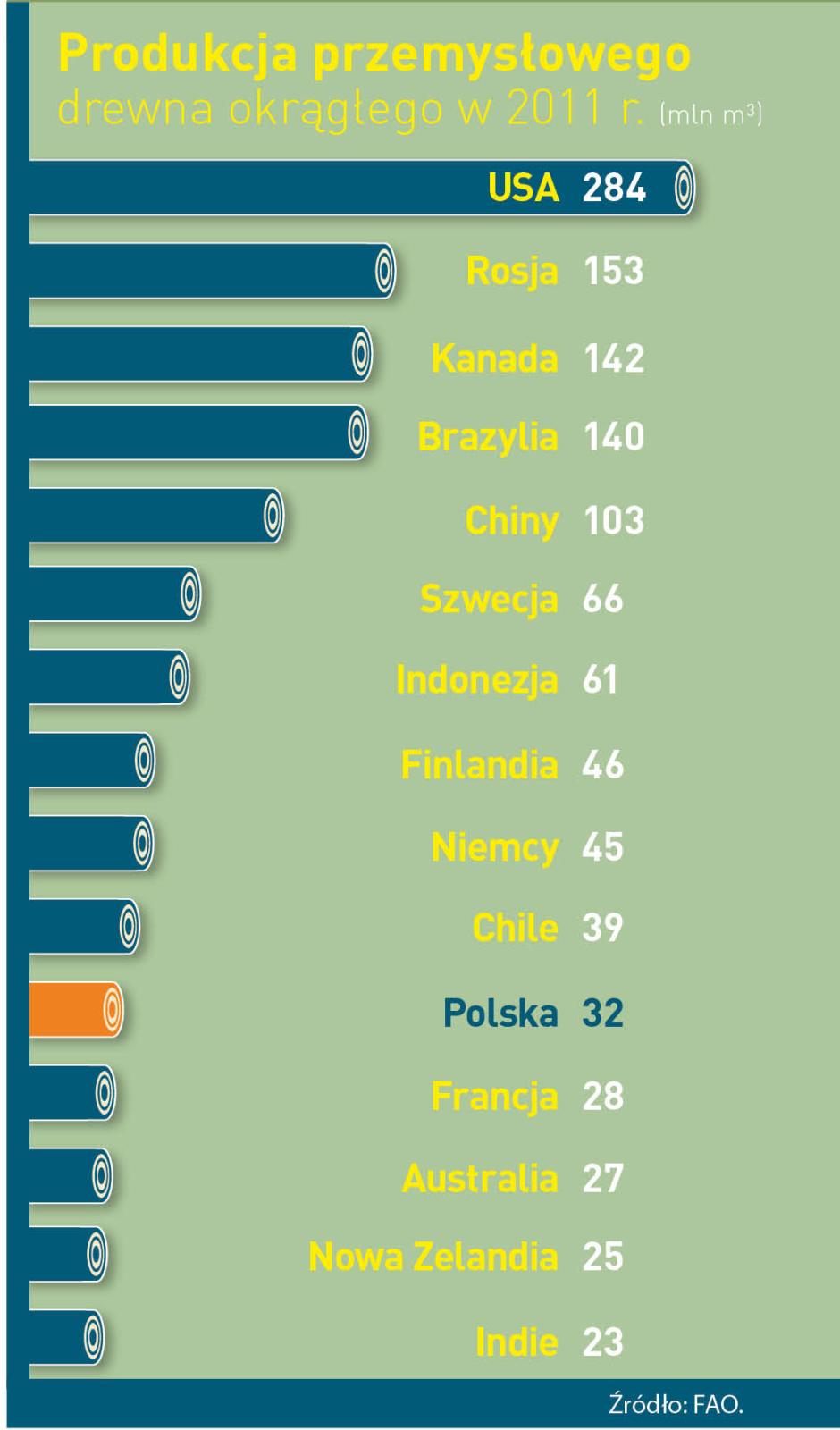
Our country is the is the 10 largest producer of furniture and the 4 largest furniture exporter in the world. Wood industry sells abroad goods of its approximate value of 45 million zl annually, what constitutes 10 % of the whole Polish export. The measurement of the essential role of forestry and timber based sector in our management is that, it works out about 2 % of GDP (Gross Domestic Product). Not only it gives work to thousands of people, but it is also an engine of investment and of development of innovative technologies. From the beginning of transformation, it drew foreign capital of its value over 30 million zl.
Forest gives work
The State Forests belong to the leading group of employers in Poland. However, both forest and timber provide for workers with several thousand of Forestry Services Companies, which within the contract of mandate deal with, among others, planting trees and their nursing, wood logging and its transportation. And above all cooperate with people employed in several dozen thousand of companies creating wood and furniture industry and paper manufacture. Summing up, it gives as many as 375 thousand of Poles altogether. Statistically, every hundred inhabitant of our country works in the sector connected with forestry and wood processing.
Among private companies of forestry and timber based sector, there are also big companies with the share of foreign capital , and big and medium sized indigenous companies, but 9 of 10 companies in this sector are small plants employing less than 10 people. These are often family companies, cultivating multigenerational traditions connected with forestry and working in less developed regions of the country. There, forestry and wood industry, as well as agriculture constitute the basis of maintaining hundred thousand of families. As many as 600 % of all working places in the forest and wood based sector are located within rural areas.
Forest and wood based sector works out about 2 % of Polish GDP (Gross Domestic Product).
- 2 % of Polish GDP works out forest and wood based sector .
- Poland takes 4 place as the largest furniture exporter and 10 place as the largest producer of furniture.
- 50 % of paper and 9 of 10 pieces of furniture produced in Poland is exported abroad
- The value of annual export of Polish goods of wood and furniture industry and paper manufacture equals 45 billion zl (it is 10 % of the whole export).
- 30 billion zl , as direct foreign investments, have been drown since 1990 by Polish wood based sector (5,5 % of all).
- 100 kg of paper is used annually by statistic Pole (an average of UE is 160 kg, for USA – 230 kg).
Source: E. Ratajczak „Potencjał gospodarczy przemysłów opartych na drewnie i perspektywy ich rozwoju (Economic performance of wood – based industries and perspectives of their development)", GUS, Warszawa 2012.
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
HISTORY
HISTORY
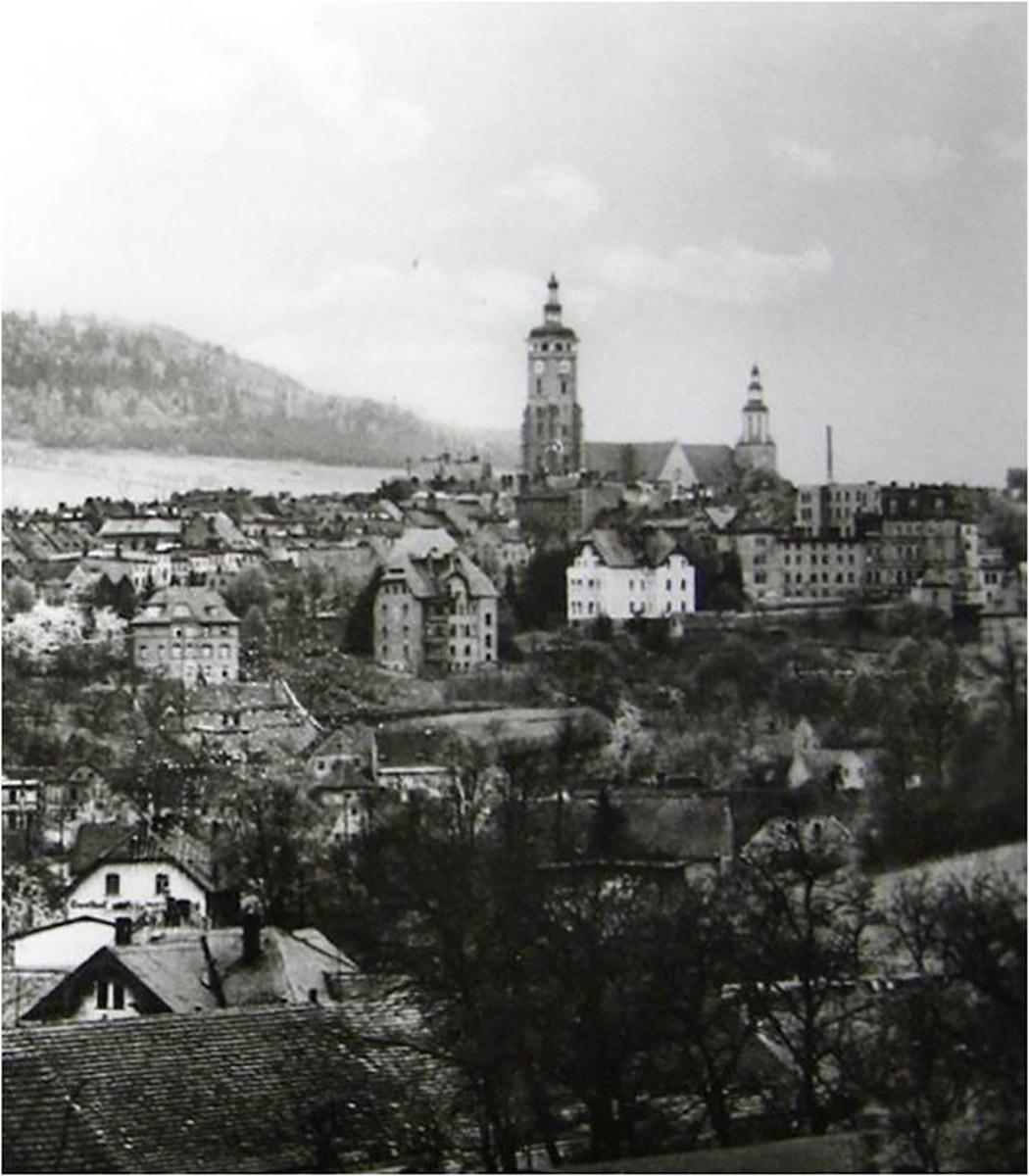
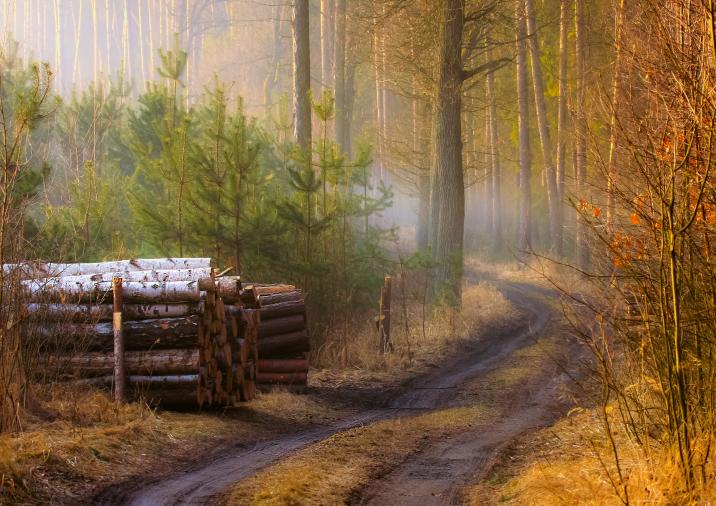
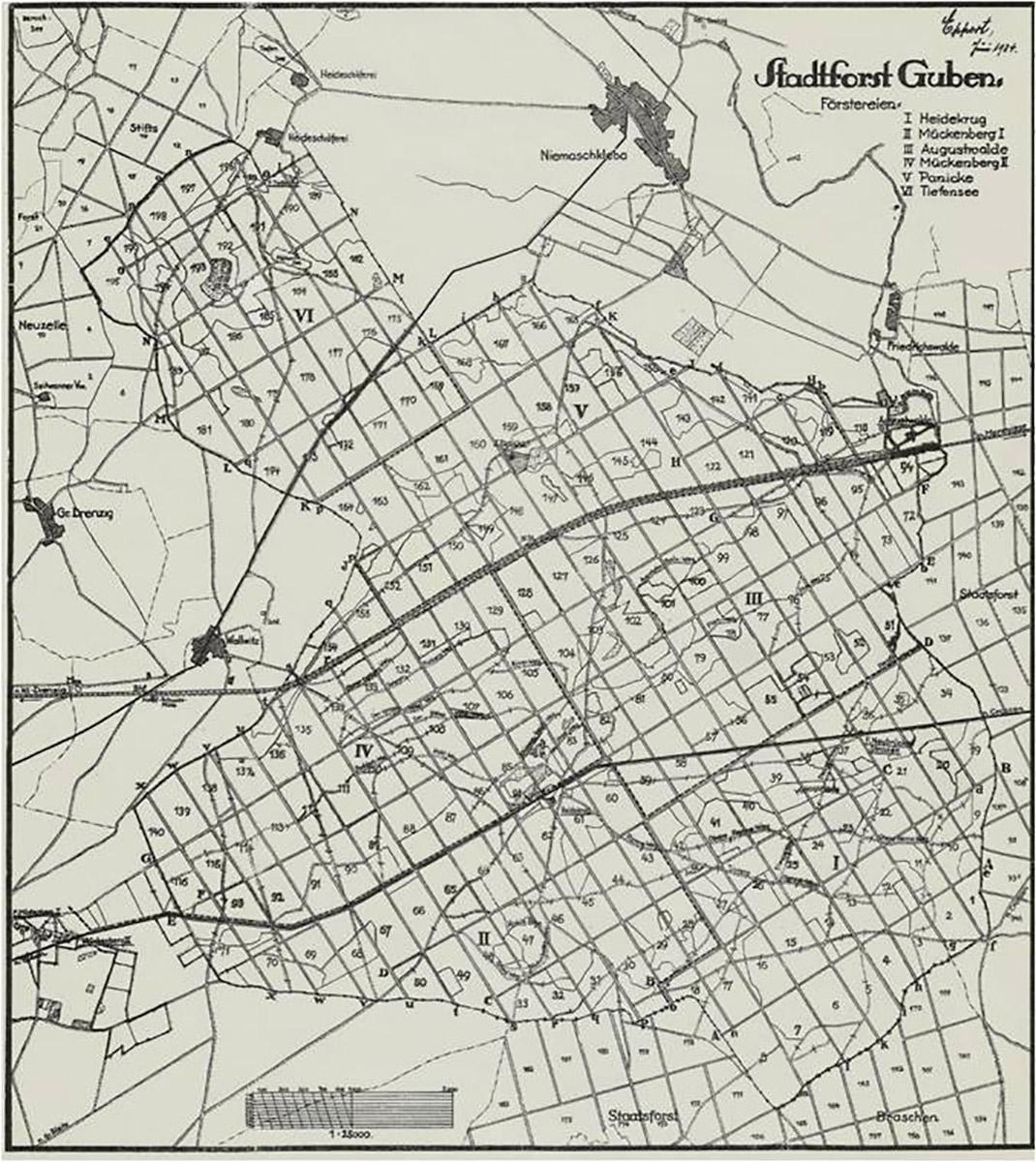
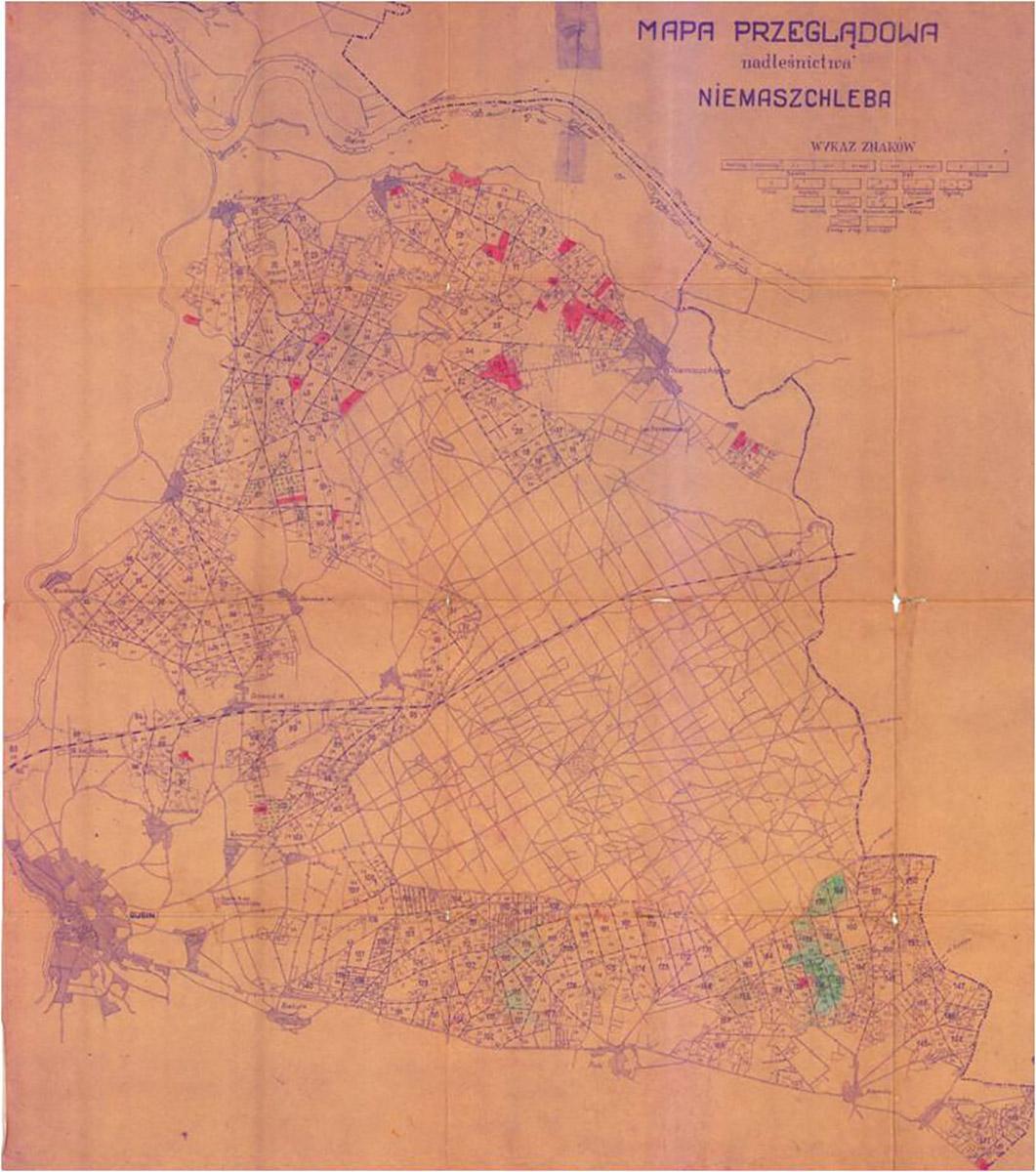
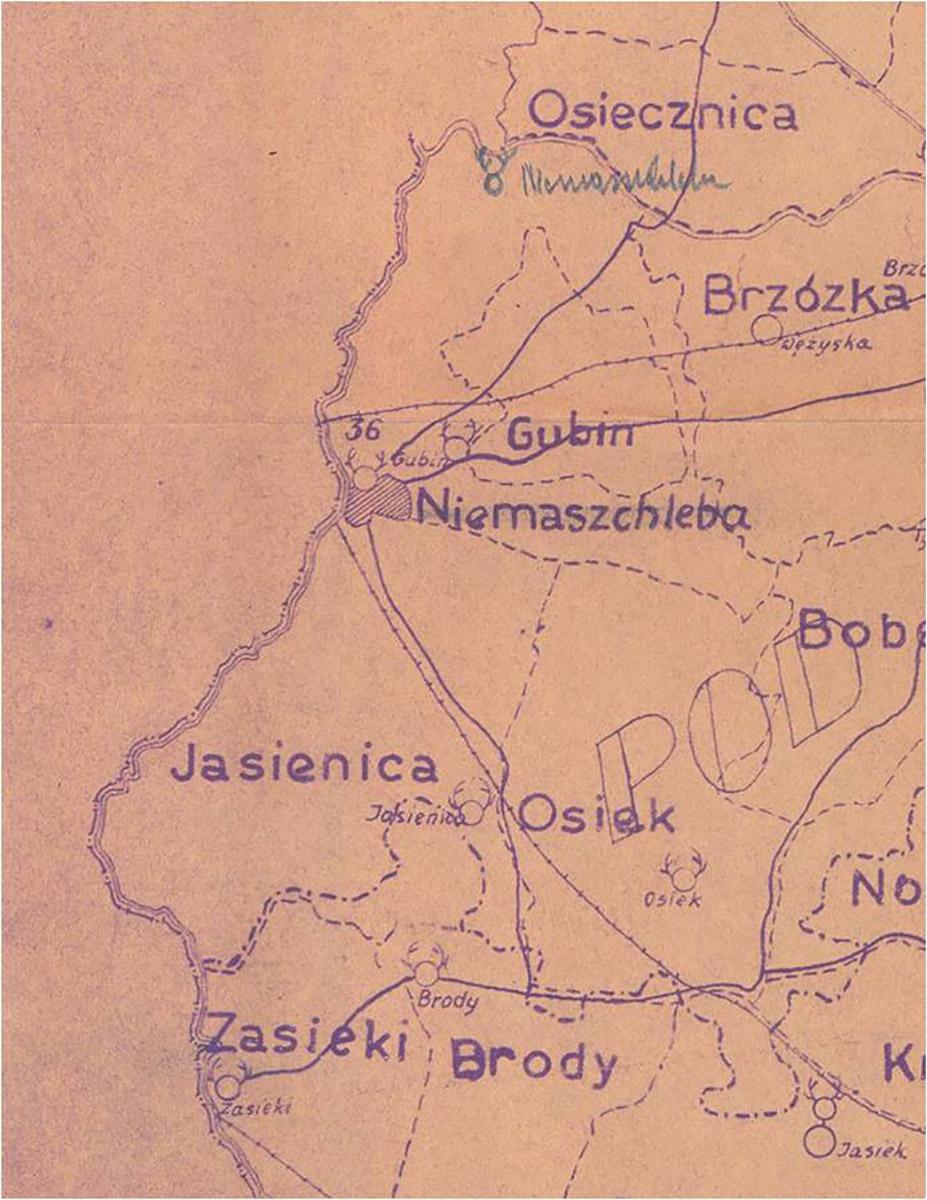
In 1286 the town of Gubin made a trade transaction that benefited the town and its growth for centuries, becoming its main source of income. The residents of Gubin have bought the Tholmer village, together with all its rights, outbuildings and adjacent land, from Henry the Illustrious. Although the village had been destroyed by the Husites, it was surrounded by valuable forests and meadows. The village was located around present-day Dzikowo, 8 km east of Gubin. Over the centuries, the purchase of the land proved to be a more and more valuable investment. It was a beginning of municipal forest growing on picturesque hills. The purchase was a well-founded move as the town could only expand to the east then (other directions were managed by monasteries).
In 1726 the residents of Gubin lodged a complaint on the authorities of the town on the matter of mismanagement of the municipal forests. The complaint had to do with allowing many villages to pick wood from the forests and the profit that could have been much higher. After the intervention the authorities limited wood picking (to two days a week) and made it available only for the residents of Gubin. In 1822 a forest deputation was created to manage the forest (it included the mayor, a member of the council and four residents; later also a head forester).
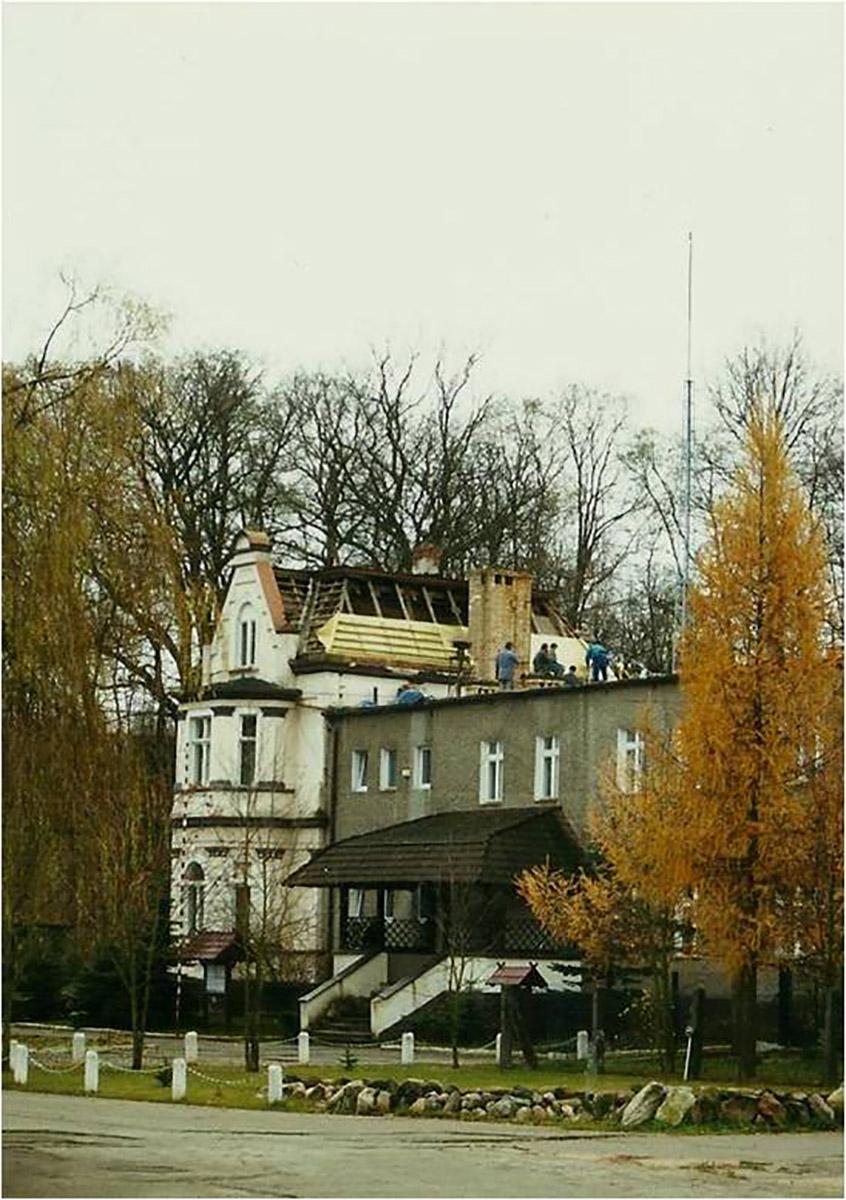
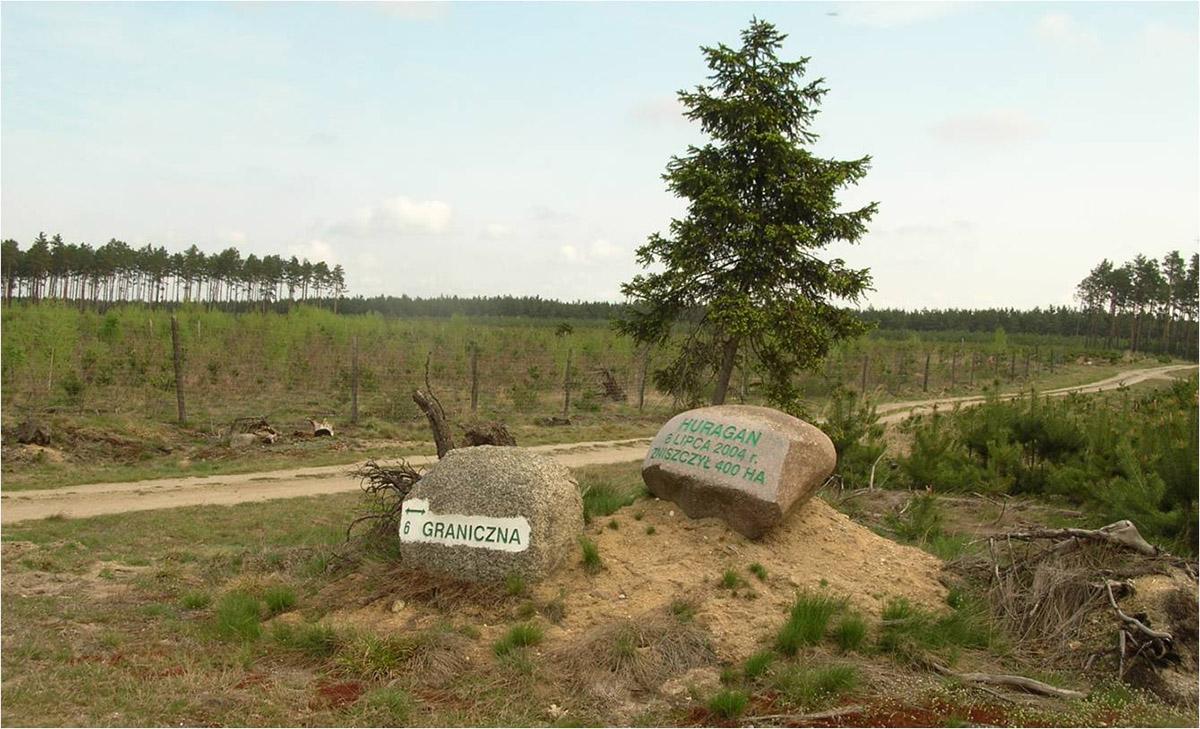
On 25 May 1830 a powerful storm has passed through the town and the forest. Around 140 thousand trees were blown down. The effects of the storm were visible for 10 years. The wood from the trees that were blown down was used for repairs of damaged buildings. In turn, in 1840 huge fires has hit the forest.
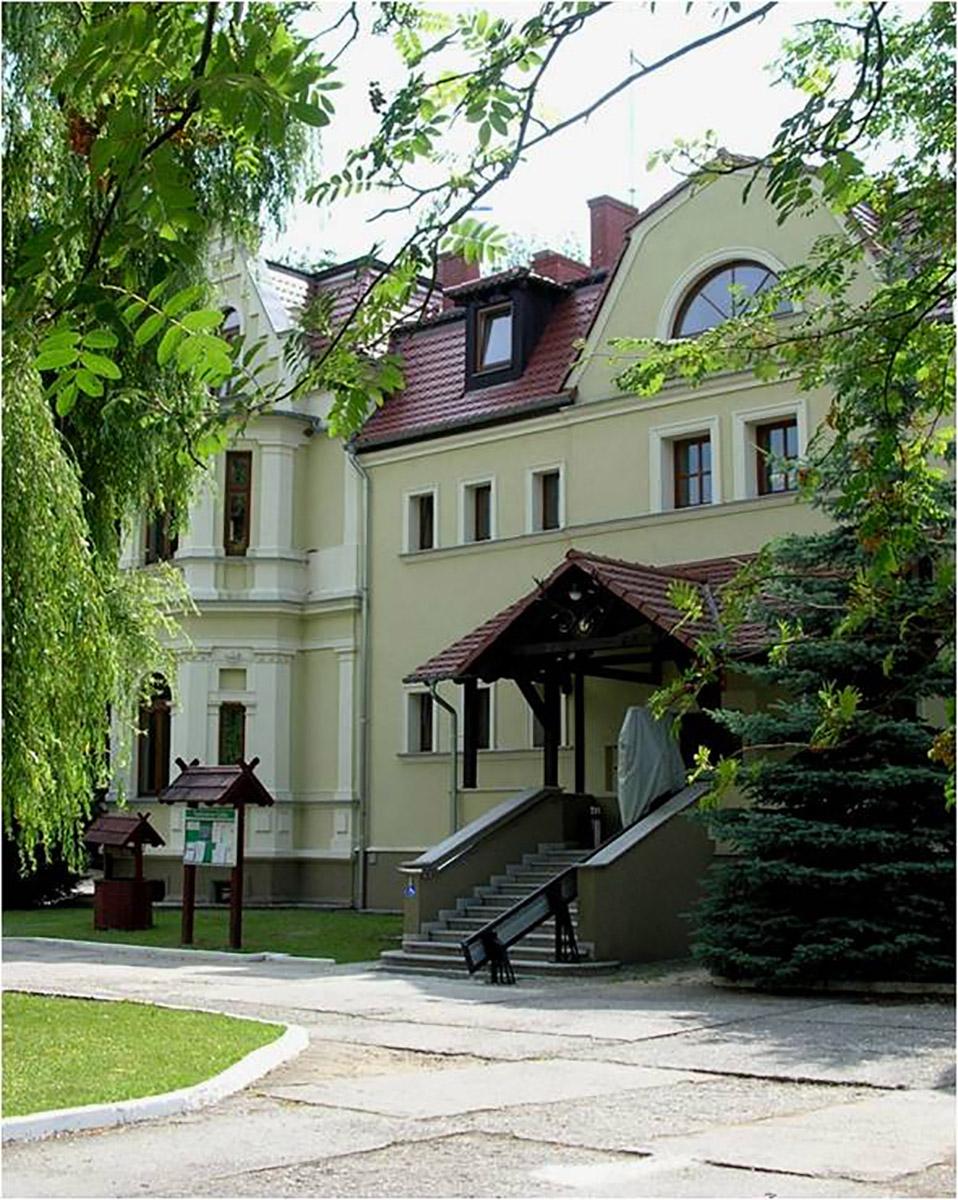
After that period, the forest management became more profitable and all the town districts were developing thanks to wise decision of the then mayor Bothmer. Dzikowo Forest District headquarters was built and the first forester obtained an office apartment. In the next years Gubin was hit by a few insect plagues. Many residents had to fight the plagues and thousands of marks were spent to fight it. In 1888 exploratory drillings were made in the forests in search for brown coal, however, the results were insignificant and unprofitable. The Municipal Forest District Office in Dzikowo was open until World War II. Its building was demolished in 1999 because of modernisation of a national road.
The area of around 6000 ha of municipal forests was divided into 6 forest rangers area in those times.